前言:ThreadLocal源码学习
简介
ThreadLocal采用线程隔离的方式存放数据(存放的值是线程封闭,线程间互斥),可以避免多线程之间出现数据访问冲突。
对于同一个static ThreadLocal,不同线程只能从中get,set,remove自己的变量,而不会影响其他线程的变量。
所以ThreadLocal重要作用在于线程内(单个线程内部)的数据共享,保证各个线程间数据安全,每个线程的数据不会被另外线程访问和破坏,多线程间数据隔离
PS:个人建议先学习ThreadLocal的静态内部类ThreadLocalMap,然后再来看ThreadLocal,ThreadLocal比较简单,复杂的地方都在ThreadLocalMap 常用方法
- ThreadLocal.get: 以ThreadLocal为key获取数据。
- ThreadLocal.set: 以ThreadLocal为key存放数据
- ThreadLocal.remove: 以ThreadLocal为key删除数据。
- ThreadLocal.initialValue:
对于多线程资源共享的问题,同步机制采用了“以时间换空间”的方式,而ThreadLocal采用了“以空间换时间”的方式,使用其内部静态类ThreadLocalMap存储线程的变量
类图
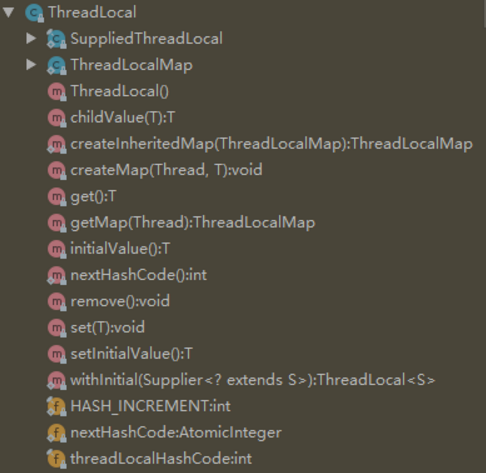
字段
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
|
SuppliedThreadLocal
SuppliedThreadLocal是ThreadLocal的一个扩展,用来支持java8函数式接口等新特性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| static final class SuppliedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
private final Supplier<? extends T> supplier;
SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) {
this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);
}
@Override
protected T initialValue() {
return supplier.get();
}
}
|
ThreadLocalMap
因为内容较多,详情见本站ThreadLocalMap源码学习一文
构造方法
默认构造方法,仅创建一个TreadLocal
1
2
| public ThreadLocal() {
}
|
childValue
childValue方法在子类InheritableThreadLocal中定义
1
2
3
| T childValue(T parentValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
|
createInheritedMap
根据传入的Map创建ThreadLocalMap
1
2
3
| static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
|
createMap
set、setInitialValue方法中被调用,创建ThreadLocalMap类对象并传入firstValue来初始化
1
2
3
| void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
|
get
常用方法,返回当前线程副本中的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
|
getMap
返回与当前线程关联的ThreadLocalMap,threadLocals是Thread的属性
1
2
3
| ThreadLocalMap (Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
|
initialValue
初始化,可以重写initialValue()来设置初始value值
1
2
3
| protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
|
nextHashCode
计算下一个hashcode
1
2
3
| private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
|
remove
删除ThreadLocal中该线程
1
2
3
4
5
| public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
|
set
设置此线程的数据,注意set传的参数是this,即当前ThreadLocal对象,所以说ThreadLocalMap是以ThreadLocal对象为key
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
|
setInitialValue
初始化,由get方法调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
|
withInitial
用于支持java8函数式编程
1
2
3
| public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) {
return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);
}
|
简单实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static final ThreadLocal<Object> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Object>();
private static final int ThreadNum = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer integer = new Integer("0");
ThreadLocalTest.threadLocal.set(integer);
if (ThreadLocalTest.threadLocal.get() != null) {
System.out.println("主线程 : " + ThreadLocalTest.threadLocal.get());
for (int i = 0; i < ThreadNum; i++) {
String name = "ThreadTask" + i;
new Thread(new MyThreadTask(name)).start();
}
}
}
public static class MyThreadTask implements Runnable {
private String name;
MyThreadTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Integer integer = new Integer("1");
ThreadLocalTest.threadLocal.set(integer);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("线程" + name + ": " + ((Integer) ThreadLocalTest.threadLocal.get() + i));
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
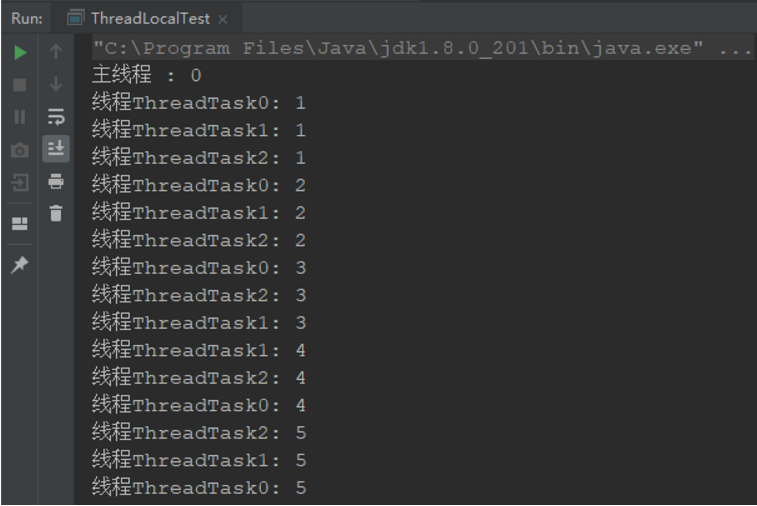
可以看到各线程中的变量都是相互独立、互不影响
总结
Thread、ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap三者关系如下图
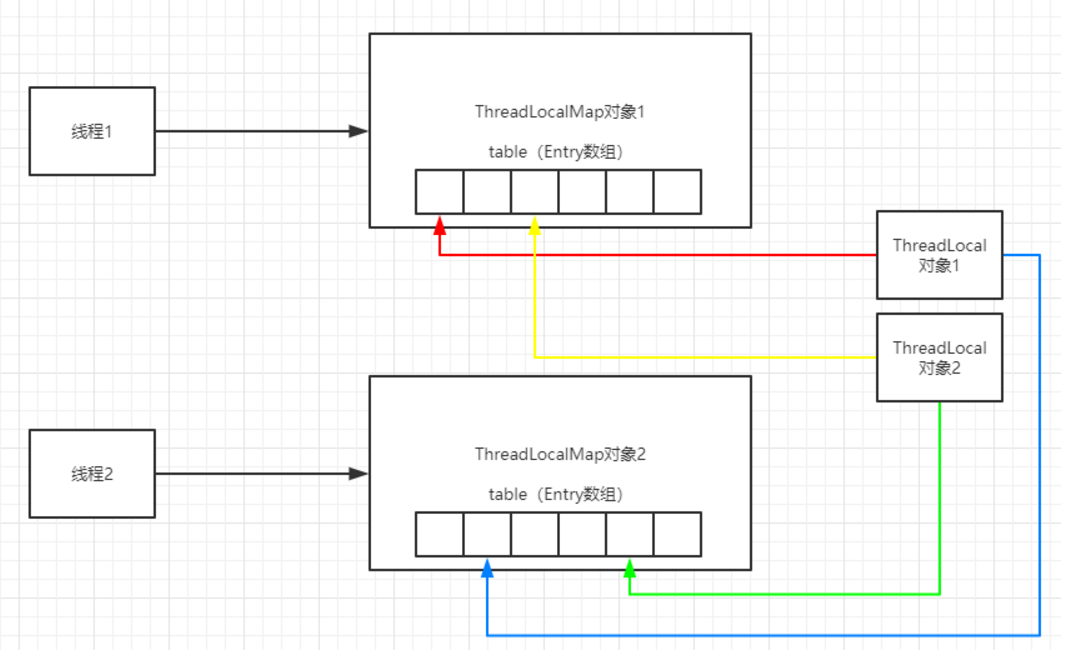
线程调用ThreadLocal对象get、set,第一次调用set时会创建一个ThreadLocalMap对象,注意这个对象是属于线程的。然后以ThreadLocal对象为key存储数据,这里也要注意


