前言:剑指offer上
二维数组中的查找 解法1:二分查找
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution public boolean Find (int target, int [][] array) for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) { int left = 0 ; int right = array[i].length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; if (array[i][mid] == target){ return true ; }else if (array[i][mid]< target){ left = mid + 1 ; }else { right = mid - 1 ; } } } return false ; } }
解法2:利用二维数组由上到下,由左到右递增的规律,那么选取右上角或者左下角的元素a[row][col]与target进行比较
当target小于元素a[row][col]时,那么target必定在元素a所在行的左边,即col–;
当target大于元素a[row][col]时,那么target必定在元素a所在列的下边,即row++;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution public boolean Find (int target, int [][] array) if (array == null ) { return false ; } int width = array[0 ].length; int height = array.length; int row = 0 , col = width - 1 ; while (row < height && col >= 0 ) { if (array[row][col] == target) { return true ; } else if (array[row][col] < target) { row++; } else { col--; } } return false ; } }
替换空格 解法1:string的replaceAll函数
1 2 3 4 5 public class Solution public String replaceSpace (StringBuffer str) return str.toString().replaceAll("\\s" , "%20" ); } }
解法2:遍历string
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution public String replaceSpace (StringBuffer str) StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length(); i++) { if (str.charAt(i) == ' ' ) { result.append("%20" ); } else { result.append(str.charAt(i)); } } return result.toString(); } }
从尾到头打印链表 链表节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class ListNode int val; ListNode next = null ; ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } }
解法1:遍历链表并储存在ArrayList中,然后反转ArrayList
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;public class Solution public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead (ListNode listNode) ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); while (listNode != null ){ list.add(listNode.val); listNode = listNode.next; } Collections.reverse(list); return list; } }
解法2:递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import java.util.ArrayList;public class Solution private ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead (ListNode listNode) if (listNode != null ){ printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next); list.add(listNode.val); } return list; } }
重建二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import java.util.Arrays;public class Solution public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree (int [] pre,int [] in) if (pre.length == 0 ||in.length == 0 ){ return null ; } TreeNode node = new TreeNode(pre[0 ]); for (int i = 0 ; i < in.length; i++){ if (pre[0 ] == in[i]){ node.left = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1 , i+1 ), Arrays.copyOfRange(in, 0 , i)); node.right = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, i+1 , pre.length), Arrays.copyOfRange(in, i+1 ,in.length)); } } return node; } }
用两个栈实现队列 一个做出队列,一个做入队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); public void push (int node) stack1.push(node); } public int pop () if (stack1.empty() && stack2.empty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!" ); } if (stack2.empty()) { while (!stack1.empty()) { stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } } return stack2.pop(); } }
旋转数字的最小数字 二分查找
需要考虑三种情况
(1)array[mid] > array[right]
出现这种情况的array类似[3,4,5,6,0,1,2],此时最小数字一定在mid的右边。
(2)array[mid] == array[right]
出现这种情况的array类似 [1,0,1,1,1] 或者[1,1,1,0,1],此时最小数字不好判断在mid左边
(3)array[mid] < array[right]
出现这种情况的array类似[2,2,3,4,5,6,6],此时最小数字一定就是array[mid]或者在mid的左
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Solution public int minNumberInRotateArray (int [] array) if (array == null || array.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int left = 0 , right = array.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; if (array[mid] > array[right]) { left = mid + 1 ; } else if (array[mid] < array[right]) { right = mid; } else { right = right - 1 ; } } return array[left]; } }
斐波那契数列 斐波那契数列指的是这样一个数列 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21……
这个数列从第3项开始,每一项都等于前两项之和。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Solution public int Fibonacci (int n) int sum = 0 , f = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { sum += f; f = sum - f; } return sum; } }
跳台阶 表面是跳台阶,实际是斐波那契数列
f(1) = 1, f(2) = 2, f(3) = 3, f(4) = 5, 可以总结出f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)的规律,但是为什么会出现这样的规律呢?假设现在6个台阶,我们可以从第5跳一步到6,这样的话有多少种方案跳到5就有多少种方案跳到6,另外我们也可以从4跳两步跳到6,跳到4有多少种方案的话,就有多少种方案跳到6,其他的不能从3跳到6什么的啦,所以最后就是f(6) = f(5) + f(4);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public int JumpFloor (int target) int sum = 1 , f = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < target - 1 ; i++) { sum += f; f = sum - f; } return sum; }
变态跳台阶
f(0) = 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public int JumpFloorII (int target) if (target == 0 || target == 1 ) { return 1 ; } int num = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= target; i++) { num = num * 2 ; } return num; }
矩形覆盖 找规律,斐波那契数列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public int RectCover (int target) if (target == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int sum = 1 , f = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < target - 1 ; i++) { sum += f; f = sum - f; } return sum; }
二进制中1的个数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Solution public int NumberOf1 (int n) int count = 0 ; String s = Integer.toBinaryString(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == '1' ) { count++; } } return count; } }
数值的整数次方 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution public double Power (double base, int exponent) if (base == 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (exponent == 0 ) { return 1 ; } double result = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i > exponent; i--) { result = result * (1 / base); } for (int i = 0 ; i < exponent; i++) { result = result * base; } return result; } }
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 新建集合存放偶数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Solution public void reOrderArray (int [] array) int len = array.length; int k = 0 ; List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { if (array[i] % 2 == 0 ) { list.add(array[i]); } else { array[k++] = array[i]; } } for (int i = k; i < len; i++) { array[i] = list.get(i - k); } } }
冒泡
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution public void reOrderArray (int [] array) for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length - 1 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (array[j] % 2 == 0 && array[j + 1 ] % 2 == 1 ) { int t = array[j]; array[j] = array[j + 1 ]; array[j + 1 ] = t; } } } } }
链表中倒数第k个结点 stack
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Solution public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode head, int k) LinkedList<ListNode> stack = new LinkedList<ListNode>(); ListNode p = head; while (p != null ) { stack.push(p); p = p.next; } if (k > stack.size() || k == 0 ) { return null ; } return stack.get(k - 1 ); } }
双指针:指针p和q,p先走K步,使两指针相差K,然后一起走,p为null时,q就是倒数第K个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Solution public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode head, int k) ListNode p = head, q = head; int count = k; while (count-- > 0 ) { if (p == null ) { return null ; } p = p.next; } while (p != null ) { p = p.next; q = q.next; } return q; } }
反转链表 三个指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution public ListNode ReverseList (ListNode head) ListNode p = head, pre = null , cur = null ; while (p != null ) { cur = p.next; p.next = pre; pre = p; p = cur; } return pre; } }
合并两个排序的链表 队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Solution public ListNode Merge (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) if (list1 == null && list2 == null ) { return null ; } LinkedList<ListNode> queue = new LinkedList<ListNode>(); while (list1 != null || list2 != null ) { if (list1 == null ) { queue.add(list2); list2 = list2.next; } else if (list2 == null ) { queue.add(list1); list1 = list1.next; } else if (list1.val < list2.val) { queue.add(list1); list1 = list1.next; } else { queue.add(list2); list2 = list2.next; } } ListNode head = queue.remove(), p = head; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { p.next = queue.remove(); p = p.next; } return head; } }
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution public ListNode Merge (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) if (list1 == null ) { return list2; } else if (list2 == null ) { return list1; } ListNode p = null ; if (list1.val < list2.val) { p = list1; p.next = Merge(list1.next, list2); } else { p = list2; p.next = Merge(list1, list2.next); } return p; } }
树的子结构 树节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class TreeNode int val = 0 ; TreeNode left = null ; TreeNode right = null ; public TreeNode (int val) this .val = val; } }
递归:判断tree1和tree2是否相同,先判断根节点是否相同,相同则调用isTreeEqual判断子节点是否相同;如果根节点不同,则判断tree1子树与tree2是否相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class Solution public boolean HasSubtree (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) if (root1 == null || root2 == null ) { return false ; } boolean flag = false ; if (root1.val == root2.val) { flag = isTreeEqual(root1, root2); } if (!flag) { flag = HasSubtree(root1.left, root2); } if (!flag) { flag = HasSubtree(root1.right, root2); } return flag; } private boolean isTreeEqual (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) if (root2 == null ) { return true ; } if (root1 == null ) { return false ; } if (root1.val != root2.val) { return false ; } return isTreeEqual(root1.left, root2.left) && isTreeEqual(root1.right, root2.right); } }
二叉树的镜像 先序遍历,交换左右子节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution public class TreeNode int val = 0 ; TreeNode left = null ; TreeNode right = null ; public TreeNode (int val) this .val = val; } } public void Mirror (TreeNode root) if (root == null ) { return ; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { return ; } TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; Mirror(root.left); Mirror(root.right); } }
顺时针打印矩阵 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Solution public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix (int [][] matrix) if (matrix == null ) { return null ; } int row = matrix.length; int column = matrix[0 ].length; ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); int circle = ((row < column ? row : column) + 1 ) / 2 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < circle; i++) { for (int j = i; j < column - i; j++) { list.add(matrix[i][j]); } for (int k = i + 1 ; k < row - i; k++) { list.add(matrix[k][column - i - 1 ]); } for (int m = column - i - 2 ; (m >= i) && (row - i - 1 != i); m--) { list.add(matrix[row - i - 1 ][m]); } for (int n = row - i - 2 ; (n > i) && (column - i - 1 != i); n--) { list.add(matrix[n][i]); } } return list; } }
包含min函数的栈 如何保存最小元素?
我们需要在最小元素弹出后还能得到次小元素, 次小的弹出后, 还要能得到次次小的.
因此, 用另一个栈来保存这些元素是再合适不过的了. 最小元素栈,每次压栈操作时,如果压栈元素比当前最小元素更小, 就把这个元素压入最小元素栈, 原本的最小元素就成了次小元素. 同理, 弹栈时, 如果弹出的元素和最小元素栈的栈顶元素相等, 就把最小元素的栈顶弹出.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Solution LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>(); LinkedList<Integer> minStack = new LinkedList<Integer>(); public void push (int node) if (minStack.isEmpty() || node <= minStack.peek()) { minStack.push(node); } stack.push(node); } public void pop () int node = stack.pop(); if (node == minStack.peek()){ minStack.pop(); } } public int top () return stack.peek(); } public int min () return minStack.peek(); } }
栈的压入、弹出序列 使用辅助栈,pushA数组逐个进栈,如果栈顶等于出栈一个元素,就pop并将pop顺序向后移动一位,最后检测辅助栈是否为空
举例:
入栈1,2,3,4,5
出栈4,5,3,2,1
首先1入辅助栈,此时栈顶1≠4,继续入栈2
此时栈顶2≠4,继续入栈3
此时栈顶3≠4,继续入栈4
此时栈顶4=4,出栈4,弹出序列向后一位,此时为5,,辅助栈里面是1,2,3
此时栈顶3≠5,继续入栈5
此时栈顶5=5,出栈5,弹出序列向后一位,此时为3,,辅助栈里面是1,2,3
依次执行,最后辅助栈为空。如果不为空说明弹出序列不是该栈的弹出顺序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Solution LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>(); public boolean IsPopOrder (int [] pushA, int [] popA) int k = 0 ; for (int i : pushA) { stack.push(i); while (!stack.isEmpty() && popA[k] == stack.peek()){ stack.pop(); k++; } } return stack.isEmpty(); } }
从上往下打印二叉树 广度搜索,使用队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class Solution public class TreeNode int val = 0 ; TreeNode left = null ; TreeNode right = null ; public TreeNode (int val) this .val = val; } } public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom (TreeNode root) ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); if (root == null ) { return list; } queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode t = queue.remove(); list.add(t.val); if (t.left != null ) { queue.add(t.left); } if (t.right != null ) { queue.add(t.right); } } return list; } }
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
二叉搜索树的特性是左子树上所有的结点均小于根结点、右子树所有的结点均大于根结点。
后序遍历是左右根,序列的最后一个元素为二叉树的根节点
基于上述特点,算法如下
确定root;
遍历序列(除去root结点),找到第一个大于root的位置,则该位置左边为左子树,右边为右子树;
遍历右子树,若发现有小于root的值,则直接返回false;
分别判断左子树和右子树是否仍是二叉搜索树(即递归步骤1、2、3)。
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Solution public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST (int [] sequence) if (sequence == null || sequence.length == 0 ) { return false ; } return judge(sequence, 0 , sequence.length - 1 ); } private boolean judge (int [] arr, int l, int r) if (l >= r) { return true ; } int i = r; while (i > l && arr[i - 1 ] > arr[r]) { --i; } for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= l; --j) { if (arr[j] > arr[r]) { return false ; } } return judge(arr, l, i - 1 ) && (judge(arr, i, r - 1 )); } }
非递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST (int [] sequence) int size = sequence.length; if (0 == size){ return false ; } int i = 0 ; while (--size >= 0 ) { while (sequence[i] < sequence[size]) { i++; } while (sequence[i] > sequence[size]) { i++; } if (i < size) { return false ; } i = 0 ; } return true ; } }
二叉树中和为某一值的路径 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution ArrayList<ArrayList><Integer>> pathList = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); public ArrayList<ArrayList><Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root, int target) { preorder(root, target); Collections.sort(pathList, (o1, o2) -> o2.size() - o1.size()); return pathList; } private void preorder (TreeNode root, int target) if (root == null ) { return ; } list.add(root.val); if (root.val == target && root.left == null && root.right == null ) { pathList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); } FindPath(root.left, target - root.val); FindPath(root.right, target - root.val); list.remove(list.size() - 1 ); } }
复杂链表的复制 第一步:复制每个结点,如复制结点A得到A1,将结点A1插到结点A后面;
第二步:遍历链表,复制老结点的随机指针给新结点,如A.next.random = A.random.next;
第三步:拆分链表,将链表拆分为原链表和复制后的链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Solution public RandomListNode Clone (RandomListNode pHead) if (pHead == null ) { return null ; } RandomListNode p = pHead; while (p != null ) { RandomListNode t = new RandomListNode(p.label); t.next = p.next; p.next = t; p = t.next; } p = pHead; while (p != null ) { p.next.random = p.random == null ? null : p.random.next; p = p.next.next; } p = pHead; RandomListNode head = pHead.next; while (p != null ) { RandomListNode cloneNode = p.next; p.next = cloneNode.next; cloneNode.next = cloneNode.next==null ?null :cloneNode.next.next; p = p.next; } return head; } }
二叉搜索树与双向链表 二叉搜索树、有序,所以选择中序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution private TreeNode head = null ; private TreeNode p = null ; public TreeNode Convert (TreeNode pRootOfTree) preorder(pRootOfTree); return head; } private void preorder (TreeNode root) if (root == null ) { return ; } preorder(root.left); if (head==null ){ head = root; p = head; }else { p.right = root; root.left = p; p = root; } preorder(root.right); } }
全排列 递归+回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class Solution private ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); public ArrayList<String> Permutation (String str) if (str != null && str.length() > 0 ) { PermutationHelper(str.toCharArray(), 0 ); Collections.sort(list); } return list; } private void PermutationHelper (char [] cs, int i) if (i == cs.length - 1 ) { String val = String.valueOf(cs); if (!list.contains(val)) { list.add(val); } } else { for (int j = i; j < cs.length; j++) { swap(cs, i, j); PermutationHelper(cs, i + 1 ); swap(cs, i, j); } } } private void swap (char [] cs, int i, int j) char temp = cs[i]; cs[i] = cs[j]; cs[j] = temp; } }
数组中出现次数超过一半的数字 如果有符合题目条件的数字,则它出现的次数肯定比其他所有数字出现的次数和还要多。
保存第一个数字,遍历数组,若与保存的数字相同,则次数加1,否则次数减1;若次数为0,则保存下一个数字,并将次数置为1。遍历结束后,再判断它是否符合条件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution (int [] array) if (array == null || array.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int len = array.length; int num = array[0 ]; int count = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++) { if (array[i] == array[i - 1 ]) { count++; } else { count--; if (count == 0 ) { num = array[i]; count = 1 ; } } } count = 0 ; for (int i : array) { if (num == i) { count++; } } return count > len / 2 ? num : 0 ; } }
最小的K个数 ArrayList + Collections.sort
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Solution public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution (int [] input, int k) ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); if (k <= 0 || k > input.length) { return list; } for (int i : input) { list.add(i); } Collections.sort(list); return new ArrayList<Integer>(list.subList(0 , k)); } }
PriorityQueue(最小堆)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Solution public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution (int [] input, int k) PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); if (k <= 0 || k > input.length) { return list; } for (int i : input) { queue.add(i); } while (k-- > 0 ) { list.add(queue.poll()); } return list; } }
连续子数组的最大和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Solution public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray (int [] array) if (array == null || array.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int len = array.length; int sum = array[0 ]; int max = array[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++) { sum = sum + array[i]; if (sum > max) { max = sum; } if (sum <= 0 ) { sum = 0 ; } } return max; } }
整数中1出现的次数(从1到n整数中1出现的次数) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Solution public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution (int n) if (n <= 0 ) { return 0 ; } long count = 0 ; for (long i = 1 ; i <= n; i *= 10 ) { long diviver = i * 10 ; long highNumber = n / (10 * i); long currentNumber = (n / i) % 10 ; long lowNumber = n - (n / i) * i; if (currentNumber == 0 ) { count += highNumber * i; } else if (currentNumber == 1 ) { count += highNumber * i + lowNumber + 1 ; } else { count += (highNumber + 1 ) * i; } } return (int )count; } }
把数组排成最小的数
将int数组转化为String数组
String数组排序,规则自定义
String数组拼接为String
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution public String PrintMinNumber (int [] numbers) if (numbers == null || numbers.length == 0 ) { return "" ; } int len = numbers.length; String[] strings = new String[numbers.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { strings[i] = String.valueOf(numbers[i]); } Arrays.sort(strings, new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare (String o1, String o2) String s1 = o1 + o2; String s2 = o2 + o1; return s1.compareTo(s2); } }); StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (String s : strings) { stringBuilder.append(s); } return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
丑数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class Solution public int GetUglyNumber_Solution (int index) if (index <= 6 ) { return index; } int m2 = 0 , m3 = 0 , m5 = 0 ; ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(1 ); while (list.size() < index) { int n2 = list.get(m2) * 2 ; int n3 = list.get(m3) * 3 ; int n5 = list.get(m5) * 5 ; int num = Math.min(n2, Math.min(n3, n5)); list.add(num); if (num == n2) { m2++; } if (num == n3) { m3++; } if (num == n5) { m5++; } } return list.get(list.size() - 1 ); } }
第一个只出现一次的字符 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Solution public int FirstNotRepeatingChar (String str) int len = str.length(); int [] letter = new int [58 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { letter[str.charAt(i) - 'A' ]++; } for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { if (letter[str.charAt(i) - 'A' ] == 1 ) { return i; } } return -1 ; } }
逆序对 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class Solution public int InversePairs (int [] array) if (array == null || array.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int [] copy = array.clone(); int count = mergeSort(array, copy, 0 , array.length - 1 ); return count; } private int mergeSort (int [] array, int [] copy, int low, int high) if (low == high) { return 0 ; } int mid = (low + high) >> 1 ; int leftCount = mergeSort(array, copy, low, mid); int rightCount = mergeSort(array, copy, mid + 1 , high); int count = 0 ; int i = mid; int j = high; int locCopy = high; while (i >= low && j > mid) { if (array[i] > array[j]) { count += j - mid; copy[locCopy--] = array[i--]; if (count >= 1000000007 ) { count %= 1000000007 ; } } else { copy[locCopy--] = array[j--]; } } while (i >= low) { copy[locCopy--] = array[i--]; } while (j > mid) { copy[locCopy--] = array[j--]; } System.arraycopy(copy, low, array, low, high - low + 1 ); return (leftCount + rightCount + count) % 1000000007 ; } }
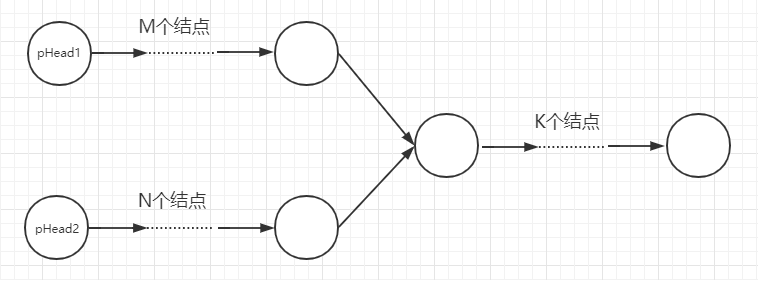
两个链表的第一个公共结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Solution public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode (ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) ListNode p1 = pHead1; ListNode p2 = pHead2; while (p1 != p2) { p1 = (p1 == null ? pHead2 : p1.next); p2 = (p2 == null ? pHead1 : p2.next); } return p1; } }
长度相同有公共结点,第一次就遍历到;没有公共结点,走到尾部NULL相遇,返回NULL
长度不同有公共结点,第一遍差值就出来了,第二遍必然一起到公共结点;没有公共,一起到结尾NULL。
也可以使用Set或Map的特性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Solution public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode (ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) HashMap<ListNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<ListNode, Integer>(); ListNode p1 = pHead1; ListNode p2 = pHead2; while (p1 != null ) { map.put(p1, p1.val); p1 = p1.next; } while (p2 != null ) { if (map.containsKey(p2)) { return p2; } p2 = p2.next; } return null ; } }